Biochar Production: Advanced Pyrolysis Systems & Biomass Gasification for Sustainable Solution
Sep 19, 2025
Biochar Production: Advanced Pyrolysis Systems & Biomass Gasification for Sustainable Solution

With global carbon dioxide emissions reaching record highs, the need for practical carbon removal technologies has never been more urgent. Modern biochar production through advanced pyrolysis systems and biomass gasification offers a scalable solution that not only sequesters carbon but also creates value from organic waste. Companies like Pyrogreen are leading this transition with engineered systems that make carbonization efficient, clean, and economically viable, transforming biomass such as forestry residues, agricultural waste, and municipal wood debris into stable carbon through biomass pyrolysis. Learn more about our biochar production technologies.
Biochar Production Technologies: Pyrolysis Reactors & Biomass Gasification Methods
Biochar Production Through Innovative Technical Pathways
The conversion of biomass to biochar relies on thermochemical processes, each with distinct mechanisms and outcomes. Advanced carbonization and torrefaction systems are designed to accommodate various feedstocks and production scales, incorporating both fundamental pyrolysis methods and specific equipment implementations:
Core Pyrolysis Technologies
Slow Pyrolysis: Operates at 350–550°C with slow heating rates, maximizing biochar yield (20–35% by weight) and ideal for carbon sequestration
Fast Pyrolysis: Focuses on liquid bio-oil production with biochar as a valuable byproduct
Gasification: Gasification: Partial oxidation at higher temperatures (700–900°C) producing syngas and biochar, enabling integrated heat and power generation through biomass gasification.
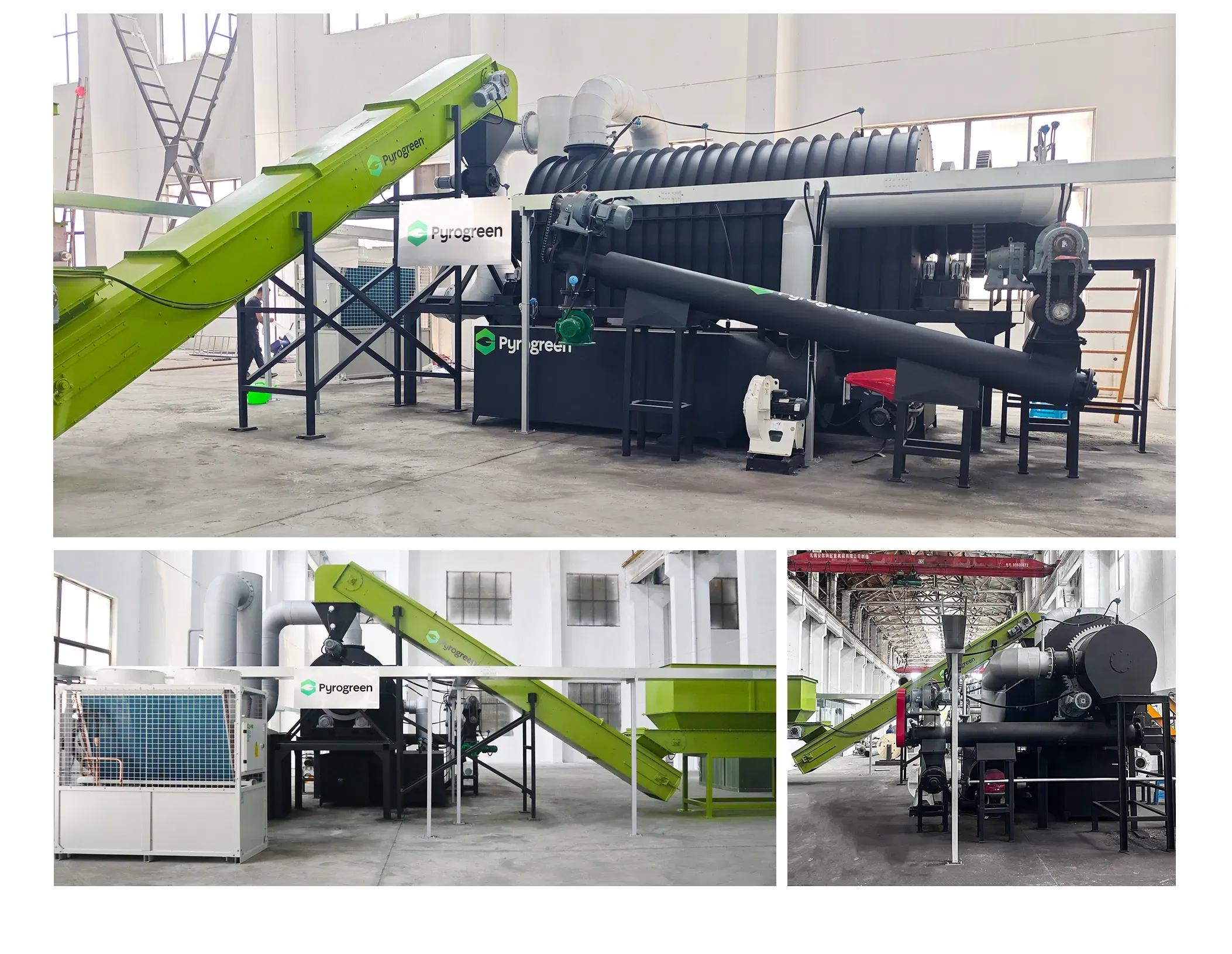
Pyrogreen Production Systems
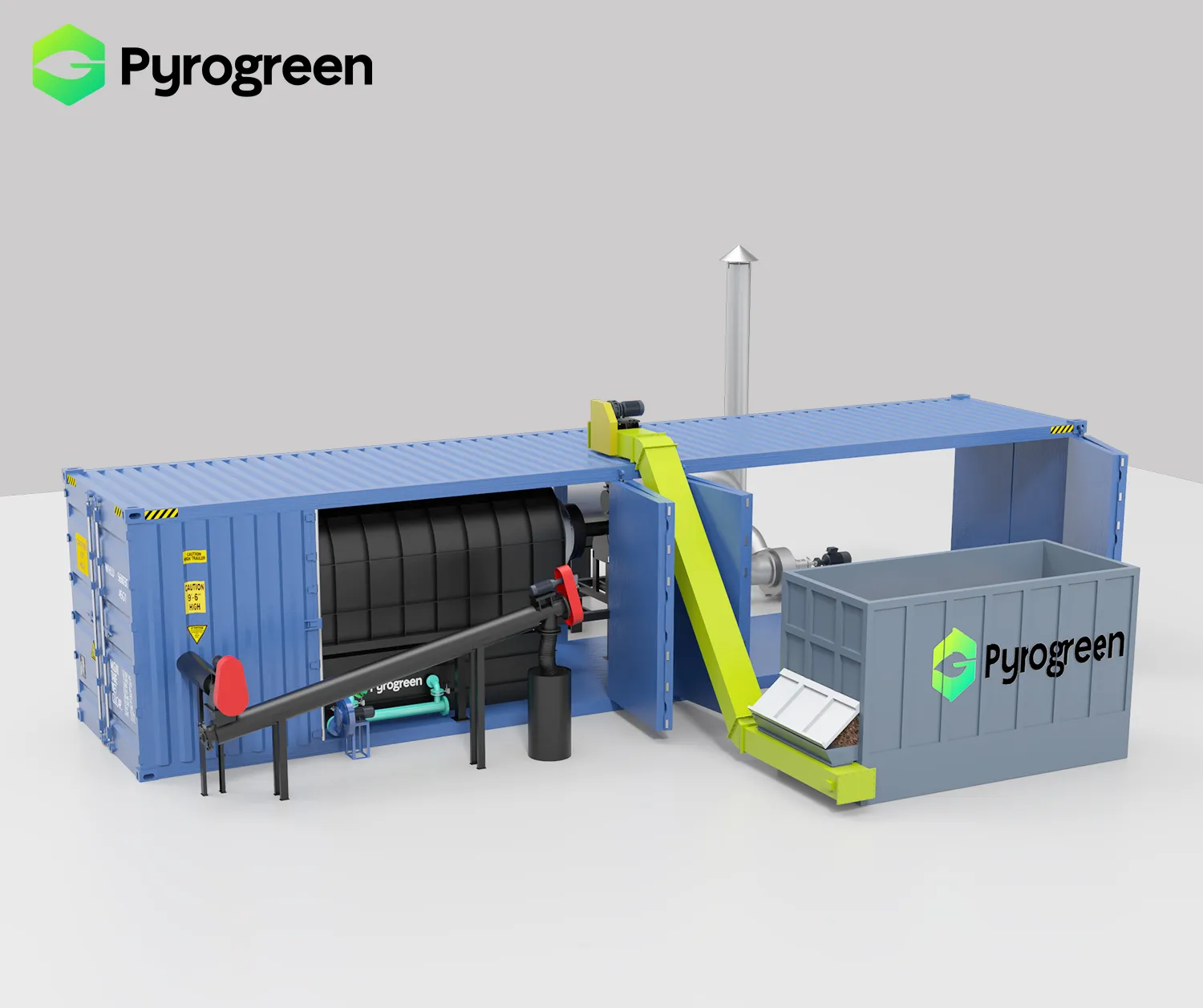 |
Screw Conveyor Biochar Production System: Utilizes an auger pyrolysis reactor for continuous processing under controlled oxygen-free conditions, representing one of the most efficient methods for biochar production |
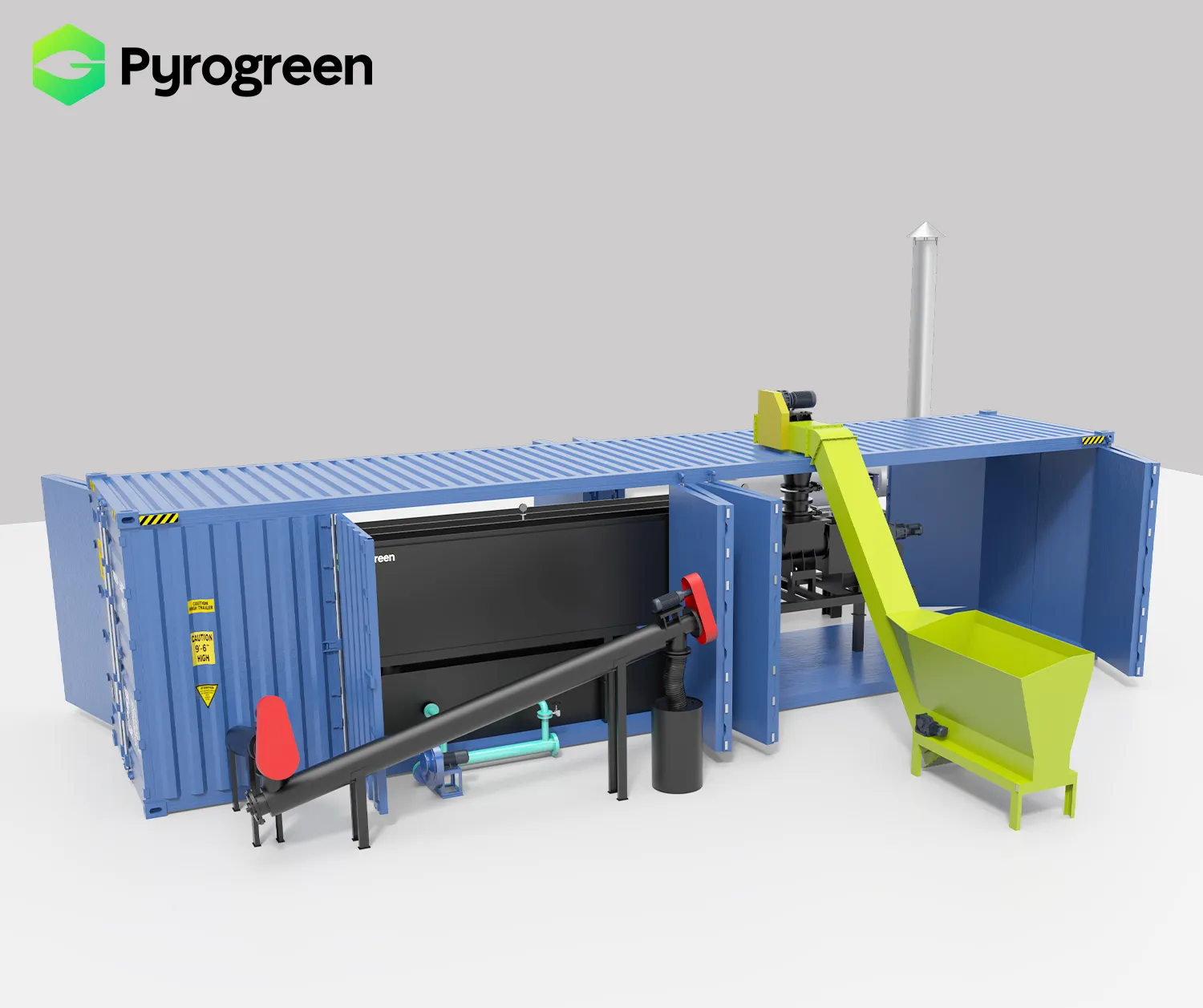 |
Rotary Kilns for Large-Scale Biochar Production: Robust solution for larger volumes and diverse biomass types enabling industrial-scale operation |
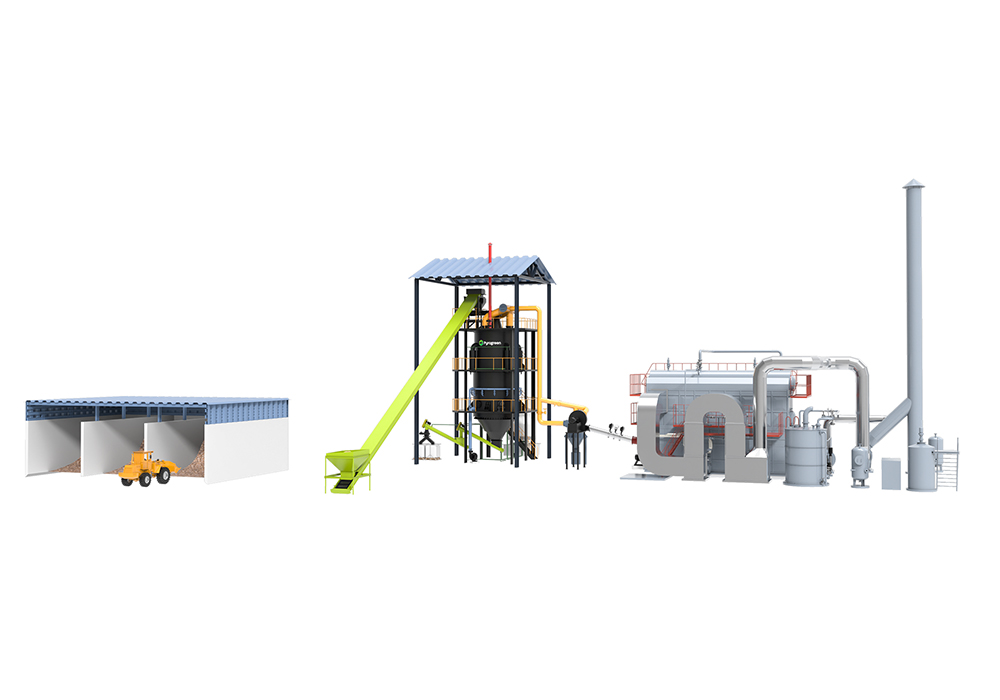 |
Fixed Bed Systems: Available in updraft and downdraft configurations, offering reliable biochar production for specific applications |
Advanced Equipment for Modern Biochar Production
Modern systems represent the cutting edge in biochar production technology, with Pyrogreen's equipment offering particularly advanced features:
System Capabilities and Scale
Small-Scale Systems: Portable biochar kilns (0.1–2 tons/day) suitable for onsite use
Medium-Scale Mobile Units: Skid-mounted pyrolysis reactors (1–10 tons/day) relocatable to biomass sources
Industrial-Scale Facilities: Fixed-site plants processing 100+ tons/day, often with combined heat and power
Technical Advantages
Diverse Applications of Modern Biochar Production

Advanced technology enables multiple value streams across environmental, agricultural, and industrial sectors:
| Environmental Applications | |
| Carbon Sequestration | Biochar contains stable carbon that persists in soils for centuries |
| Waste Management | Diverts biomass from open burning or landfills, reducing methane emissions |
| Water Treatment | Filters contaminants including heavy metals and pesticides from runoff |
| Agricultural Benefits | |
| Soil Enhancement | Improves water retention, nutrient cycling, and crop yields, particularly in degraded soils |
| Composting | Accelerates decomposition and improves compost quality when added to organic waste |
| Industrial Uses | |
| Energy Generation | Syngas production for process heat and electricity |
| Materials Production | Added to concrete, asphalt, or plastics to reduce carbon footprint |
| Thermal Applications | Syngas used for various heating and industrial processes |
Strategic Advantages of Advanced Biochar Production
Modern systems offer compelling advantages that make biochar production increasingly attractive:
|
|
Environmental Impact | |
| Carbon Negative Operations | Creating net-negative emissions through carbon sequestration | |
| Ecological Resilience | Enhancing soil biodiversity and reducing fertilizer leaching | |
| Economic Benefits | ||
| Economic Viability | Turning low-value biomass into marketable products | |
| Energy Independence | On-site syngas production reducing external energy needs | |
| Market Access |
Qualifying for carbon credits and premium markets through certifications | |
| Operational Excellence |
||
| Environmental Compliance |
Meeting stringent emission standards while eliminating waste | |
| Operational Flexibility |
Modular systems adaptable to various scales and locations | |
| Technical Innovation |
Continuous improvement in carbon conversion efficiency and cost reduction | |
The Path Forward: Scaling Biochar Production
With CO₂ emissions continuing to rise, advanced biochar production technologies offer a practical path to scale carbon removal while creating economic value. Lifecycle assessments show biochar systems can achieve net negative emissions up to 1.2 tonnes of CO₂ equivalent sequestered per tonne of dry feedstock. The growing carbon markets and certification programs provide monetization pathways for carbon removal, supporting the economic viability of these systems.
As technology continues to advance through innovation in pyrolysis reactor design and supportive policies develop, biochar production is poised to play a critical role in the global transition to a sustainable, low-carbon economy. These systems demonstrate how biomass conversion can be both environmentally responsible and commercially attractive, creating jobs in rural areas through biomass collection and biochar production while adding value to low-value biomass and reducing waste disposal costs.
Ready to explore biochar production? Modern systems offer solutions for every scale and feedstock type. Join the growing movement of organizations turning waste into worth while making measurable climate impact.
Transform your biomass into climate solutions with biochar production technology that's ready today. Whether you're a land manager, investor, policymaker, or researcher, now is the time to engage with the biochar industry by exploring equipment options, investing in production systems, or advocating for supportive policies. Together, we can build a more resilient and climate-smart future.
















