Biochar Production Equipment Manufacturer | PyroGreen Energy
Aug 20, 2025
Biochar Production Equipment Manufacturer | PyroGreen Energy

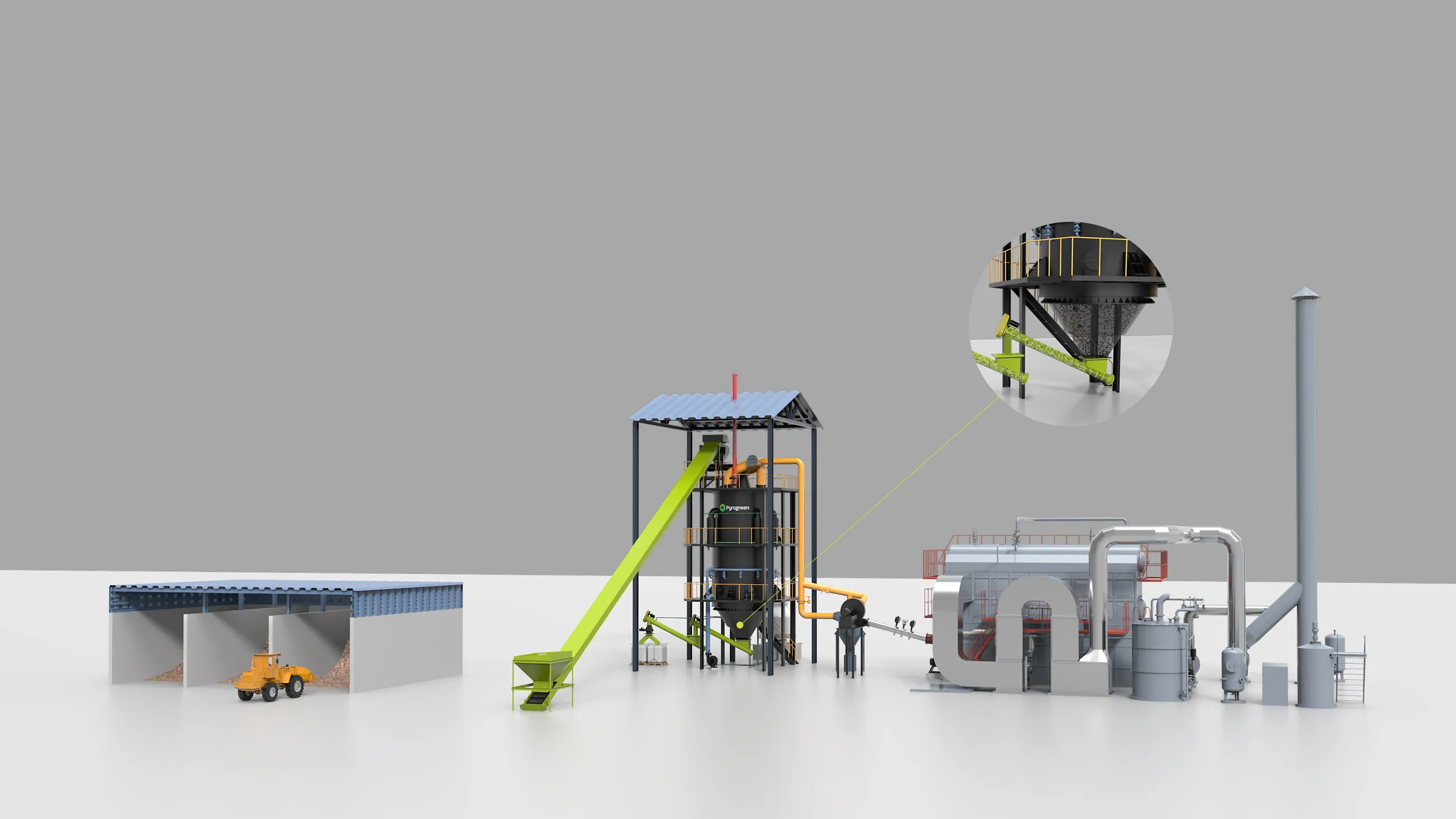
Biochar production equipment :A high-efficiency solution for converting agricultural waste into biochar through pyrolysis technology.
Bochar production equipment is an integrated system that converts biomass into biochar through a controlled pyrolysis biochar production process. Biochar production equipment has become a popular solution for processing agricultural and forestry waste. PyroGreen's biochar production machine enables large-scale, highly automated, and low-emission production of biochar, transforming agricultural and forestry residues into high-value biochar and biochar by-products energy, achieving resource recycling and carbon neutrality goals.
PyroGreen Energy: Biochar Production Equipment Manufacturer
PyroGreen Energy is a leading biochar equipment manufacturer, providing advanced solutions for sustainable carbon removal and renewable energy.
Our biochar production equipment is designed for both small biochar production equipment and industrial-scale applications, helping customers transform agricultural waste, forestry residues, and other biomass into high-value biochar and clean energy.
we provide professional biochar production solutions. Contact us to obtain a customized biochar production facility tailored to your agricultural and forestry waste needs.Explore How PyroGreen Energy Can Tailor a Biochar Solution for Your Business. 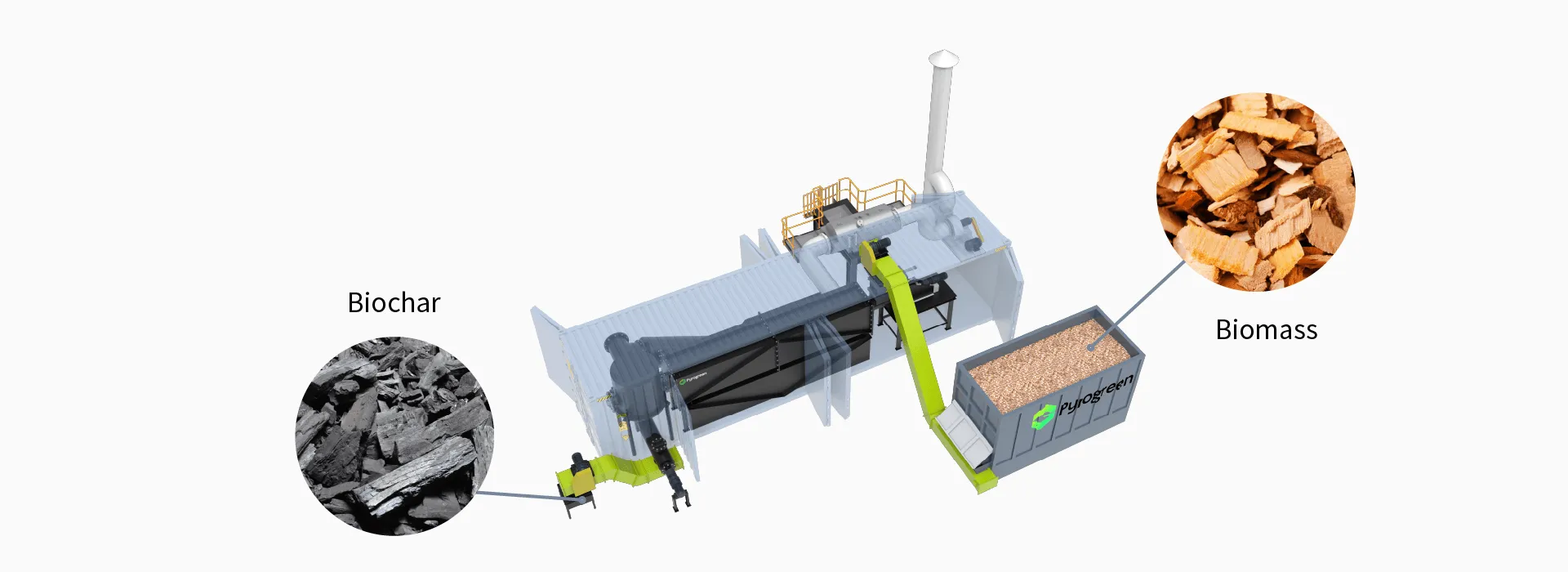
Biochar Production Equipment – A Solution for Converting Agricultural and Forestry Waste into Energy
What is Biochar Production Equipment?
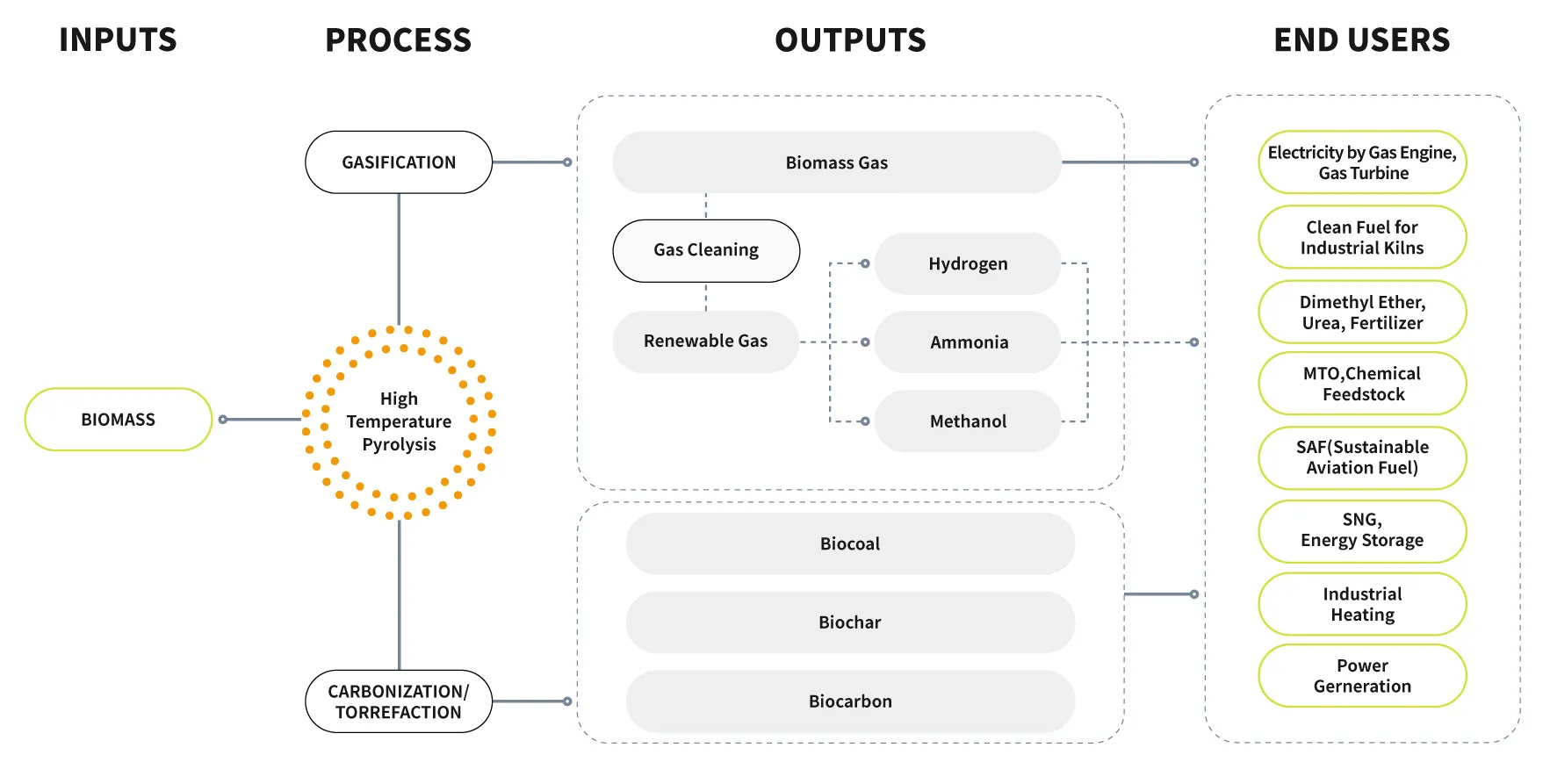
Biochar production equipment (also called biochar pyrolysis equipment or biomass carbonization equipment) is a system that converts biomass into biochar, syngas, and heat under high-temperature, oxygen-free conditions.
PyroGreen’s equipment ensures efficient biomass conversion with low emissions, producing high-quality biochar and syngas suitable for carbon removal projects, agriculture, and renewable energy recovery.
We provide tailored biochar production solutions based on your specific biomass feedstock and processing capacity, supporting both small-scale and large-scale production needs while achieving waste reduction and resource recovery.

Pyrogreen Energy can provide advanced biochar solutions and efficient ways to obtain carbon credits. Our biochar production equipment creates significant value for investors:
|
|
|
|
Inquire Now to Translate These Benefits into Your Actual Returns.
Parameter & Model of Biochar Production Equipment
|
|
|
 |
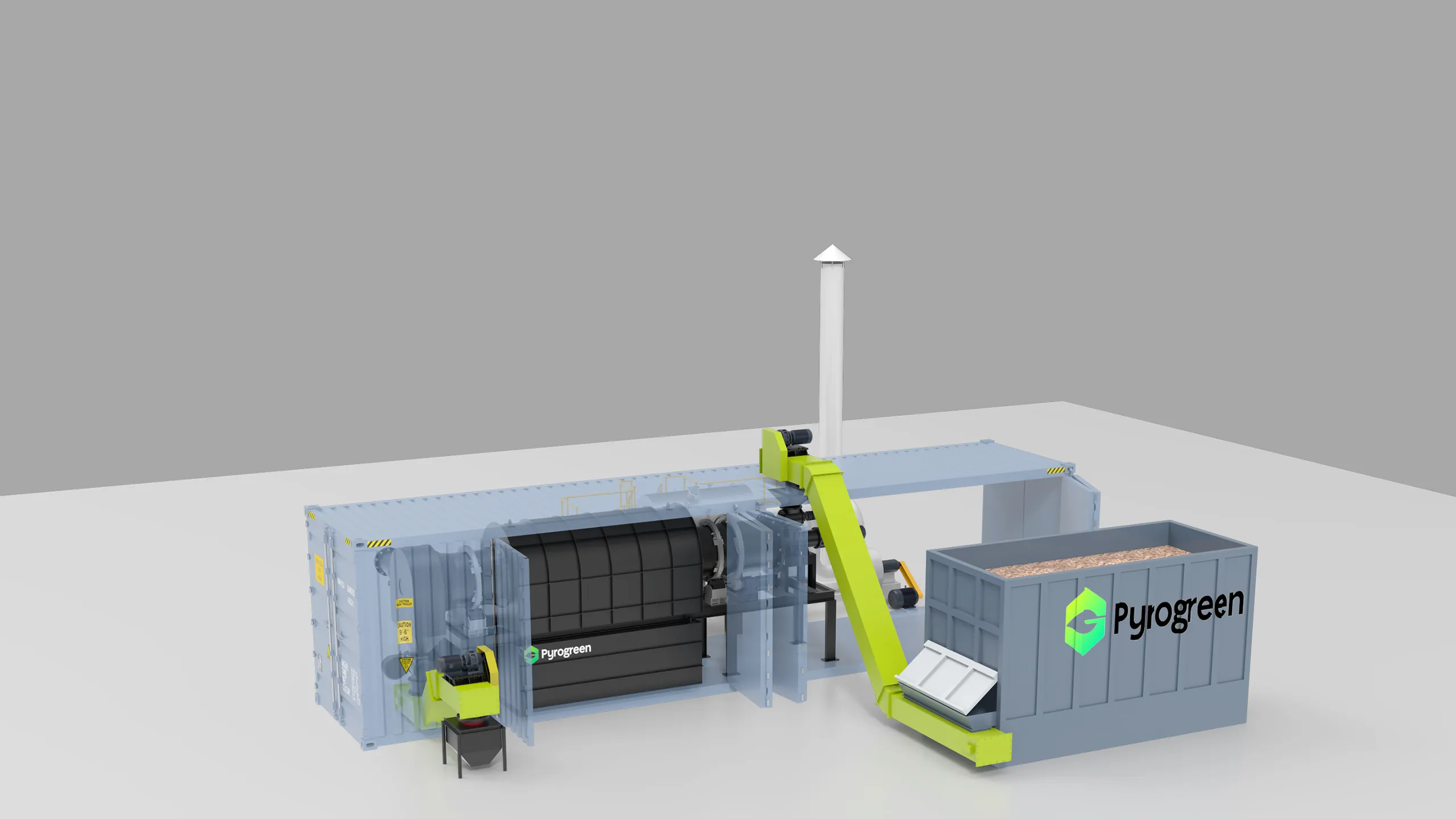 |
|
|
|
 |
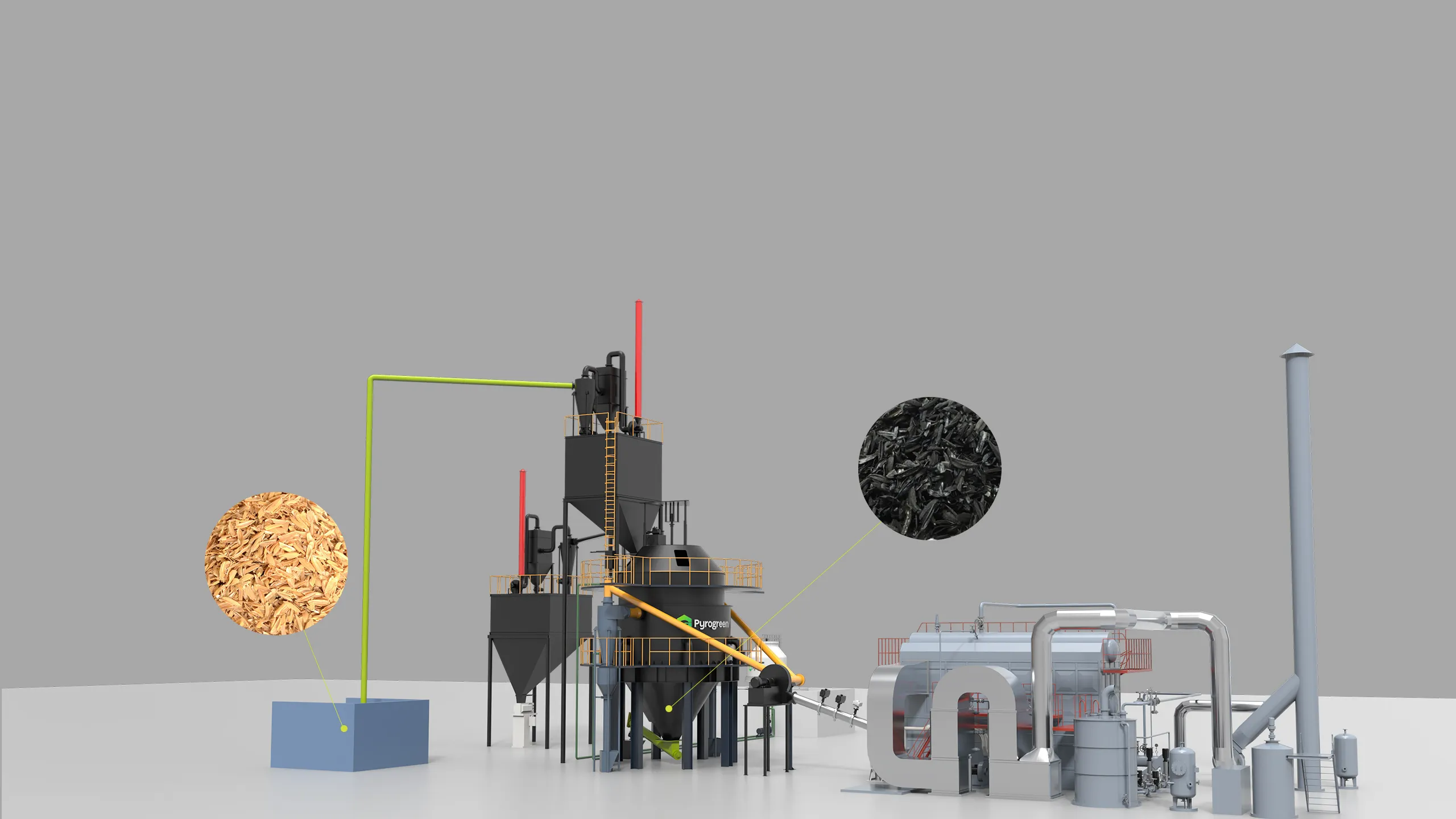 |
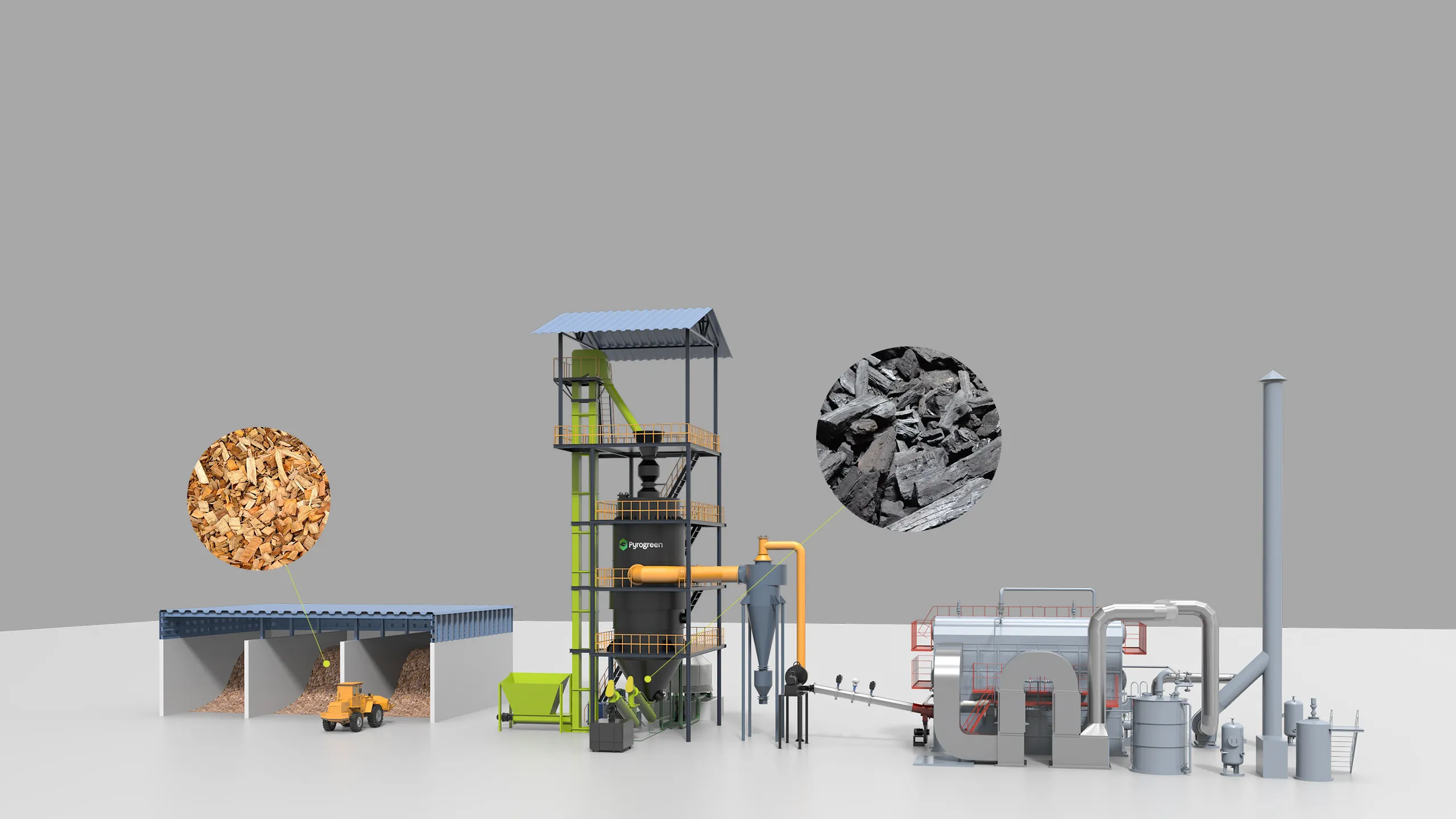 |
Biochar Production Systems Comparison
1. Biomass Screw Conveyor Carbonizer (BSCC Series)
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Model | BSCC Series |
| Processing Type | Efficient Continuous Processing |
| Feed Rate | 1~5 m³/h (300~1500 kg/h) |
| Ideal For | Small to medium-scale continuous biochar production. |
| Footprint | Compact design, 16m~21m length, space-saving. |
| Temperature Control | Precise PLC control system + indirect heating screw conveyor ensures uniform material heating. |
| Raw Material Adaptability | Handles biomass with particle size ≤20mm (optimal 5~8mm) and moisture ≤15% (e.g., wood chips, straw). |
| Fuel Options | Multi-fuel options: Compatible with diesel, natural gas, heavy oil, etc., offering flexible energy adaptation. |
| Applications | Ideal for small-scale biochar production or torrefied biomass projects requiring stable, continuous operation with limited space. |
Get Detailed Technical Specifications and Quotation.
2. Biomass Rotary Kilns Carbonizer (BRKC Series)
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Model | BRKC Series |
| Processing Type | Large-Scale Processing |
| Feed Rate | 0.6~5 m³/h (200~1500 kg/h) |
| Designed For | Industrial-scale biochar production. |
| Carbonization | Uniform high-temperature carbonization. Rotary kiln design + indirect heating ensures complete biomass pyrolysis. |
| Construction | Low-maintenance structure: SS310S + carbon steel construction, resistant to high-temperature corrosion and long-lasting. |
| Control System | Automated Control: PLC system enables full-process monitoring and user-friendly operation. |
| Material Tolerance | High material tolerance: Processes diverse biomass with particle size ≤50mm and moisture ≤15%. |
| Applications | Suited for large-scale biochar production, high-capacity demands, or projects processing coarse materials (e.g., nut shells, wood blocks). |
Get Detailed Technical Specifications and Quotation.
3. Updraft Fixed Bed Carbonizer (UFBC Series)
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Model | UFBC Series |
| Key Output | High-Quality Syngas: Produces gas with calorific value >1,200 Kcal/Nm³, directly usable for heating or power generation (biochar is a by-product). |
| Particle Handling | Large-Particle Handling: Processes bulk biomass (20~100mm) like wood chips, bamboo, coconut shells. |
| Moisture Tolerance | High Moisture Tolerance: Accepts raw materials with ≤30% moisture, reducing preprocessing costs. |
| Capacity | Modular Capacity: Biochar production output ranges from 1,000~5,000 kg/h, with customizable models. |
| Safety | Safe Negative-Pressure Operation: Micro-negative pressure design prevents gas leaks, ensuring safety. |
| Applications | Ideal for projects requiring combined biochar and syngas production, or processing high-moisture/large-particle biomass (e.g., agroforestry waste utilization). |
Get Detailed Technical Specifications and Quotation.
4. Downdraft Fixed Bed Carbonizer (DFBC-BC/S & DFBC-BC/B Series)
| Feature | Description | DFBC-BC/S Series | DFBC-BC/B Series |
|---|---|---|---|
| Model | Series Overview | S Series | B Series |
| Key Output | Low-Tar Syngas: Downdraft design significantly reduces gas tar content (calorific value 1,000~1,100 Kcal/Nm³), ideal for clean energy applications. | ||
| Material Size | Particle Size Handling | 20~80mm | Designed for high output |
| Moisture | Moisture Tolerance | ≤20% | See application |
| Example Materials | Suitable Feedstocks | e.g., rice husk, straw | |
| Biochar Output | Production Capacity | 250~550 kg/h (simultaneous with gas) | 750~2,000 kg/h (suitable for commercial production) |
| Energy Output | Syngas Heat Output | Gas heat output up to 3,488KW, recyclable for process heating. | |
| Key Benefit | Return on Investment | Dual Output enhances ROI by producing both biochar and combustible gas. | Designed for high output, enhancing ROI for commercial biochar production. |
Get Detailed Technical Specifications and Quotation.
Biochar: A Multifunctional Material from Biomass
Biochar is a type of solid material produced through the high-temperature slow pyrolysis of biomass under anaerobic conditions. It is derived from biomass, a widely available and renewable energy source, which includes forest residues, agricultural residues, municipal solid waste, urban waste, energy crops, and animal manure.
.webp)
Depending on the source of the biomass feedstock, biochar can be categorized into wood charcoal (e.g., pine charcoal, fir charcoal, oak charcoal, eucalyptus charcoal, etc.), bamboo charcoal (e.g., moso bamboo charcoal, rigid bamboo charcoal, spotted bamboo charcoal, etc.), straw charcoal (e.g., rice straw charcoal, wheat straw charcoal, cotton stalk charcoal, corn stalk charcoal, etc.), and livestock manure charcoal (e.g., pig manure charcoal, cattle manure charcoal, chicken manure charcoal, etc.).
Distinguishing Biochar from Other Carbon Materials :
| Name | Differences and Application Description |
|---|---|
| Biochar | Produced from biomass through pyrolysis technology, primarily used for soil amendment, carbon sequestration and emission reduction, and contaminated environmental remediation. |
| Char | Generally refers to carbonized materials formed by natural fires under uncontrolled conditions. |
| Charcoal | Primarily uses wood or coal as raw materials, emphasized for applications as fuel, industrial heat source, deodorization, and decolorization, possessing high calorific value and specific surface area. |
| Activated Carbon | Treated at high temperatures (>700°C) with physical or chemical activation processes, resulting in high specific surface area and strong adsorption capacity. Commonly used for pollution remediation and environmental engineering treatment. |
| Black Carbon (Black Char) | A broad term referring to residues generated from the incomplete combustion of organic matter, encompassing various carbonaceous materials such as carbon black, biochar, activated carbon, etc. Often discussed in environmental science as an atmospheric pollutant. |
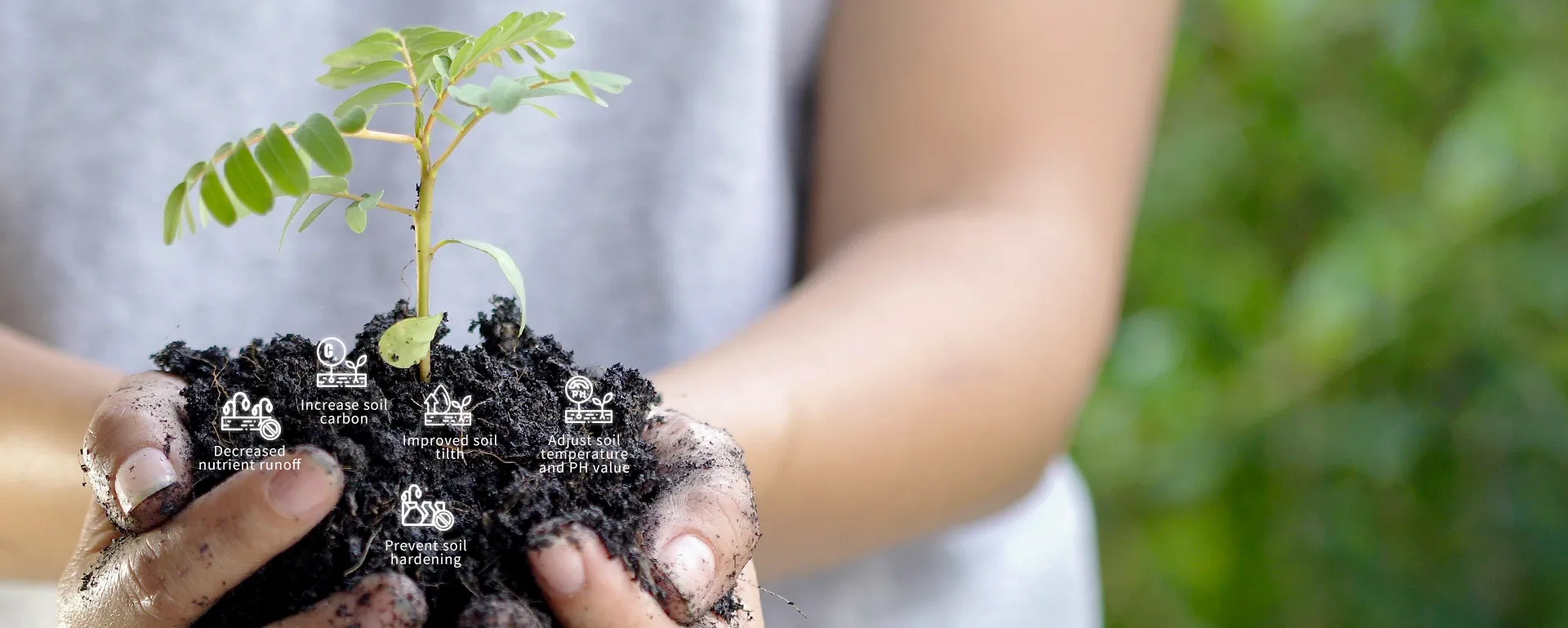
Biochar enables long-term carbon sequestration, generating high-value carbon credits. The fundamental value of biochar lies in its powerful carbon dioxide removal (CDR) capacity. Plants capture atmospheric CO₂ through photosynthesis; when they decompose naturally or are burned, this carbon is rapidly released back into the atmosphere. However, when converted into biochar, the highly stable carbon structure can persist in the soil for hundreds to thousands of years, achieving durable carbon sequestration.
This process not only reduces atmospheric CO₂ concentrations but also generates high-value carbon removal credits. These credits enter the carbon trading market, providing significant economic returns for biochar projects and incentivizing the development of the entire industrial chain from agricultural waste management to carbon sequestration.
 |
Application of Biochar in Agriculture Biochar significantly improves soil fertility and nutrient cycling. Its porous structure reduces soil density, enhances aeration, and increases water retention in sandy soils, while promoting root growth in clay soils. Additionally, its alkaline nature helps neutralize acidic soils, raising pH levels and mitigating toxic ions like aluminum and manganese. Biochar acts as a nutrient reservoir due to its high cation exchange capacity, absorbing elements such as ammonium and potassium to minimize leaching and improve fertilizer efficiency. It also supports microbial habitats, boosting both activity and diversity. Furthermore, it aids in reducing agricultural pollution by immobilizing pesticides and heavy metals, thus protecting crop safety and water quality. |
 |
Application of Biochar in Environmental Remediation Biochar effectively immobilizes heavy metals through mechanisms like surface precipitation and ion exchange within its porous structure. It also adsorbs organic pollutants such as pesticides and industrial chemicals. This high adsorption capacity makes it suitable for treating contaminated soil and water, including applications in wastewater management and rehabilitation of polluted sites. |
 |
Application of Biochar in Energy Storage Activated biochar serves as a sustainable material for supercapacitor electrodes and lithium-ion battery anodes, thanks to its high surface area, adjustable pores, and conductivity. Doping with heteroatoms can further enhance its electrochemical properties. Scaling production from lab to industry remains a key challenge to meet growing demand for eco-friendly energy storage. |
 |
Application of Biochar in the Construction Sector Biochar's low thermal conductivity makes it an effective insulator. Mixed into building materials, it enhances thermal resistance, lowering energy use for heating and cooling. It also regulates indoor humidity due to its high moisture absorption. Integrating biochar into structures supports healthier indoor air and extends carbon storage over the building's lifespan. |
 |
Application of Biochar in Forestry and Ecological Restoration In forestry, biochar amends degraded soils, supplying carbon and improving conditions for seedling establishment in stressful settings such as droughts. It also supports reforestation and land recovery efforts. Converting forest waste into biochar on-site reduces wildfire risks and turns residues into a valuable product. |











